Hi All
Hope this post find you in good health and spirit. Windows 10 has lot of exciting security feature and Credential Guard or Windows Defender Credential Guard is one of mostly used security feature. There are so many posts already on credential guard so what’s need to add one more? Most of them were long and too technical(atleast for me 🙂 ) so I thought to write a post myself. I will try to keep this simple and to-the- point.
What is Credential Guard ?
You all know SSO. Once user has logged in and provided his credential, don’t have to provide his credential again to access other resources. His credential is cached and is used to access other resources. So what will happen if someone gets access to this cached credential? He can use it to exploit resources not only on the same machine but throughout environment. Stealing credential is called credential theft and then getting access to resources throughout environment using stolen credential is called lateral traversal.
Windows Defender Credential Guard is a security feature introduced in Windows 10 and Windows Server 2016 which uses virtualization-based security to isolate secrets in order to prevent credential theft. Enabling credential guard ensures that only privileged system software have access to secrets.
How Credential Guard works?
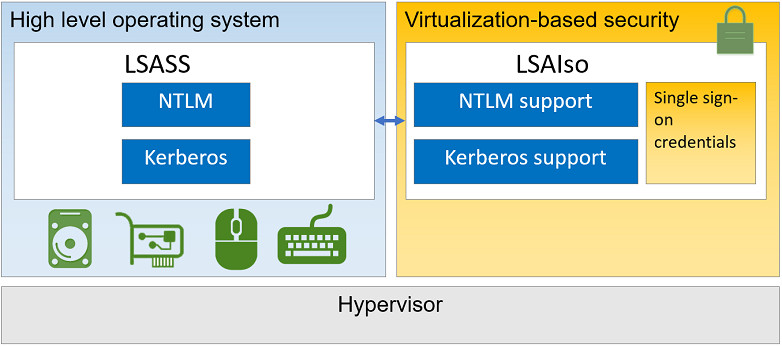
Local Security Authority (LSA) is protected subsystem that authenticates and logs users onto the local system. In previous versions of Windows (before Windows 10 and Server 2016), LSA stored secrets used by the operating system in its process memory. As discussed above, when hackers compromise operating system, they can get access to process memory leading to credential theft and lateral theft.
Credential guard uses virtualization-based security and creates a new component LSA Isolated to store all secrets that the operating system cannot access directly so that even if hackers compromise the system, they cannot do credential theft. Once Credential guard is configured, LSA process (LSASS) runs in the operating system, and additional instance of LSA (LSAIso – which stands for LSA Isolated) is created. LSA connects to LSA Isolated using RPC. This is to allow all of the standard calls to LSA to still succeed, offering backwards compatibility for services or applications that require direct communication with LSA.
Credential Guard requirement
- Operating System – Windows 10 Enterprise, Windows 10 Education, Windows Server 2016, and Windows 10 IoT Enterprise.
- Support for Virtualization-based security includes: 64-bit CPU, CPU virtualization extensions(Intel – VT or AMD-V) plus Extended page tables also called Second Level Address Translation (SLAT) and Windows hypervisor
- Secure boot
- TPM 2.0 either discrete or firmware – preferred
- UEFI lock – preferred
Consideration
- Credential Guard is supported for Hyper-V virtual machine.
- Enabling Credential Guard on domain controllers is not supported.
- Post Windows 10 1607 enabling Hyper-V Windows features is not necessary.
Configuring Credential guard
Windows Defender Credential Guard can be enabled either by using Group policy, the registry, and Windows Defender Credential Guard hardware readiness tool. Group policy is preferred way to configure Credential guard in enterprise so in this post we will discuss this method only. Configuration steps are as under:
- From the Group Policy Management Console, go to Computer configuration – Administrative Templates – System – Device Guard.
- Double-click Turn On Virtualization Based Security, and then click the Enabled option.
- In the Select Platform Security Level box, choose Secure Boot or Secure Boot and DMA Protection.
- In the Credential Guard Configuration box, click Enabled with UEFI lock, and then click OK. If you want to be able to turn off Windows Defender Credential Guard remotely, choose Enabled without lock.
 Configuration steps using registry and hardware readiness tool can be checked here:
Configuration steps using registry and hardware readiness tool can be checked here:
Credential guard limitation
Nothing is without limitation and here is what you should not expect from credential guard:
- Protection of local and Microsoft Accounts
- Protection of credentials managed by a third party software
- Protection against Key loggers
Known issues with Credential guard is logged here:
Okay, so that’s all in this post. I will soon share another post on device guard. Stay tuned and till then ta-ta.
